What Happens When The Two Programs Holding Up The Banks, BTFP And RRP, End?
March 2024 looms as a pivotal month in banking, with the Fed’s critical decisions potentially triggering a domino effect in the financial sector.
If you didn’t know the Federal Reserve is still adding billions every month as a stimulus to support the banking system? This major action has mostly gone unnoticed by most news outlets.
This represents a kind of quiet crisis in banking. It started, made little noise, and then faded away, leaving many people unaware of the ongoing financial issues. When banks started having problems in March 2023, the Federal Reserve (the Fed) stepped in to reshape the financial environment. The Fed often steps in like this to support and adjust the financial system.
The Fed responded with two main programs: the Bank Term Funding Program (BTFP) and Reverse Repurchase Agreements (RRP). The big question now is whether these actions by the Fed really solve the main problems or are they just temporary fixes.
Looking Back At 2022-2023
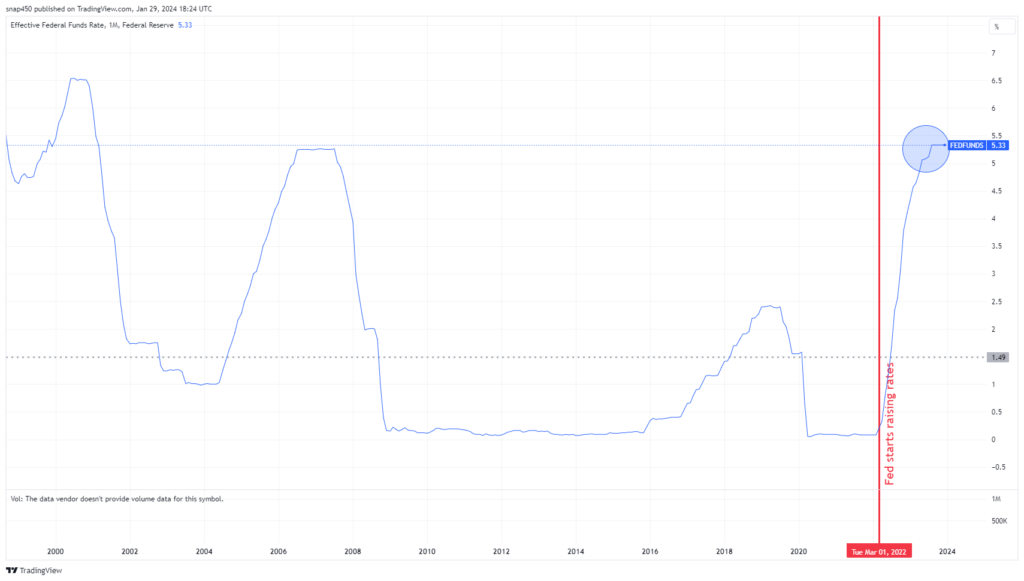
In March 2022, as inflation was a big concern, the Fed started to increase interest rates from a historically low 0.08%. These rates had been very low for 13 years since the financial crisis of 2008-2009.
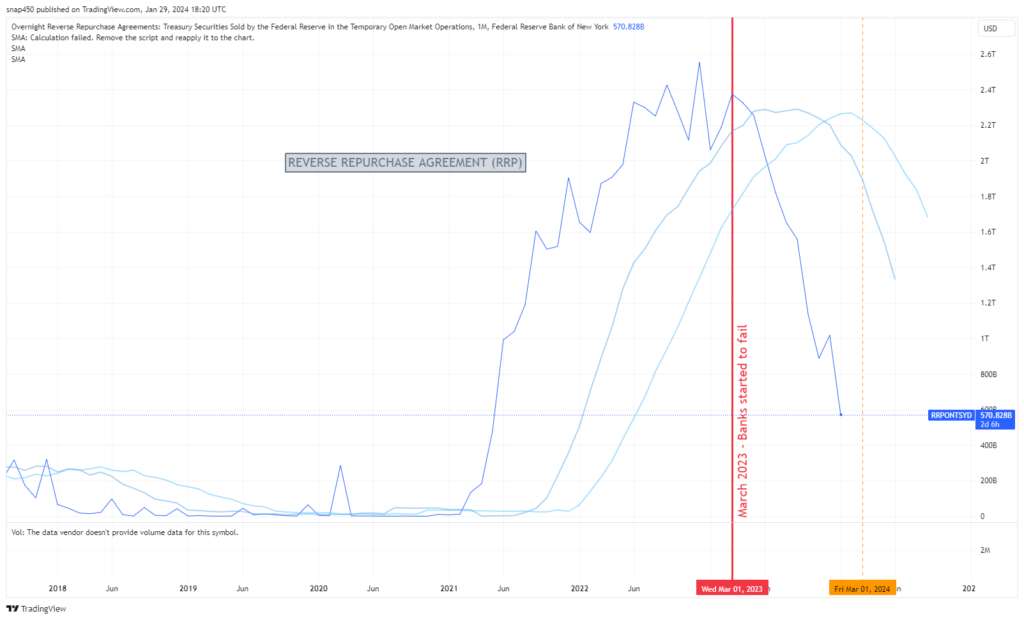
The Fed raised rates quickly because inflation was getting out of control. One method the Fed used to take liquidity out of the system and get short term rates up was with the Reverse Repurchase Agreement (RRP), in which it sold treasury securities to banks for cash. This tool was aggressively utilized starting May 2021 to remove excess liquidity and raise interest rates. By December 2022, the RRP operation had escalated to $2.5 trillion in treasury securities sold.
By March 2023, interest rates had gone up to 4.65%. The quickness of these interest rate rises uncovered weaknesses in the banking system and things spiraled out of control.
The Start Of The Crisis
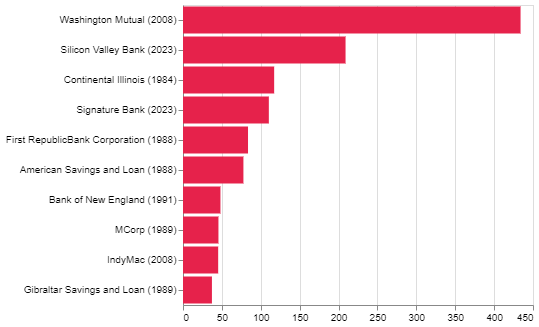
The crisis began in March 2023 shortly after the collapse of the cryptocurrency exchange FTX, which turned out to be a huge fraud. This led to the failure of Silvergate bank, which was quickly followed by Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) facing troubles. One bank after another started failing.
The Main Cause
The main reason for the crisis was the sudden increase in interest rates. For example, SVB had put a lot of its depositors’ money in low-interest treasury securities. When interest rates went up quickly, the value of these bonds dropped, reducing their market value. SVB, offering low deposit rates, faced a lot of people taking their money out. Also, when banks started to fail, depositors feared that having money in smaller banks could be risky since their deposits were only insured up to $250,000. Given this fear of failure, depositors moved their money to larger too big to fail banks such as JP Morgan. This forced SVB to sell bonds at a loss, leading to its demise.
Feds Response: BTFP and RRP
BTFP
The Fed created the BTFP to help banks with assets that lost a lot of value and were hard to sell. Under this program, the Fed gave money to banks in exchange for collateral valued at the original price, not the current lower market value. This allowed banks to get money without having to sell their assets at low prices.
Why does this matter now? Because these loans will end in March 2024 and banks will repay the loan and the Fed will give back the assets held as collateral.
RRP
At the same time, the Fed has been reducing the RRP balance, which means it’s buying back treasury securities from banks. This puts more cash into the banks and adds liquidity to the overall market. The RRP balance has been dropping for over a year and is now around $570 billion. Some think the RRP will be empty by March 2024.
What's Next: After BTFP and RRP End
As March 2024 approaches, the end of the BTFP and RRP is near, which will be a crucial time. The Fed has to decide whether to keep interest rates high to fight inflation or to ease them to help the banks. This decision will greatly impact banks and the overall market.
If the Fed lowers rates in March to help the market, inflation could stay higher for longer. But if the Fed keeps rates as they are, the lack of support from the BTFP and RRP, combined with high rates, could lead to some banks failing. This might cause more consolidation in the banking sector, with big banks like JP Morgan possibly taking over smaller struggling banks.
March 2024 is shaping up to be a significant time, and the Fed’s choices will affect the future of many banks and the market’s direction.
If you found value in this and want to see more, subscribe to my free newsletter below and follow me on X @AmintaAlex